Acetals are used as protecting groups for carbonyl groups in organic synthesis because they are stable with respect to hydrolysis by bases and with respect to many oxidizing and reducing agents. They can either protect the carbonyl in a molecule (by temporarily reacting it with an alcohol) or a diol (by temporarily reacting it with a carbonyl). That is, either the carbonyl, or the alcohols, or both could be part of the molecule whose reactivity is to be controlled.
PTFE has useful mechanical properties from cryogenic temperatures at 500° F (280° C) continuous service temperatures. Its coefficient of friction is lower than almost any other material. It also has a high oxygen level.

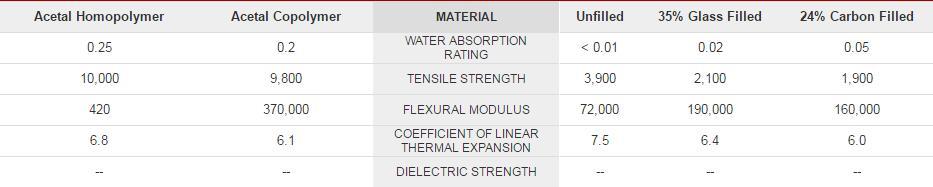
Comparison of Acetal and Polymer PTFE/FEP Property Values
Material Applications
Acetal:Bearings;Bushings;Electrical components;Gears;Rollers;Pump & valve parts.
Polymer PTFE/FEP:Cabling solutions;Non lubricated bearings;O-rings;Seals;Capacitors;Semiconductor manufacturing;High temperature electrical parts;Gaskets;Valve components.
Material Properties
Acetal:Low moisture absorption;High mechanical strength and rigidity;Machinability;Good chemical resistance;Good dimensional stability.
Polymer PTFE/FEP:Excellent dielectric properties;Inertness to most chemicals;High heat and chemical resistance;Very low coeffiecient of friction;Excellent radiation resistance;Zero moisture absorption;Relatively insensitive to power frequency;Machinability.
Post time: Nov-22-2016

